In a world where efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness reign supreme, Lean Six Sigma stands as a beacon of excellence in process improvement methodologies. Combining the principles of Lean and Six Sigma, this powerful approach empowers organizations to minimize waste, reduce defects, and enhance customer satisfaction. In this blog, we will delve into the fundamentals of lean six sigma, its key principles, methodologies, and the transformative impact it can have on your business operations.
Understanding Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a structured methodology that combines two distinct but complementary philosophies: Lean and Six Sigma.
- Lean: Lean principles, inspired by the Toyota Production System, focus on eliminating waste in processes. Waste can take many forms, such as overproduction, excessive inventory, and unnecessary waiting times. By streamlining processes and reducing waste, organizations can become more agile and responsive to customer needs.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma, on the other hand, is rooted in statistical analysis and aims to minimize defects and variations in processes. It sets a high standard, allowing only 3.4 defects per million opportunities (DPMO). Six Sigma achieves this by identifying and addressing the root causes of defects, ultimately improving process quality.
Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
- Customer-Centric Approach: Lean Six Sigma begins with a laser-sharp focus on customer requirements. Understanding and meeting these requirements are paramount to success.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Data is the lifeblood of Lean Six Sigma. It provides the evidence needed to identify problems, measure process performance, and make informed decisions.
- Continuous Improvement: The pursuit of perfection is an ongoing journey. Lean Six Sigma fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees at all levels to seek out and eliminate waste and defects.
- DMAIC and DMADV: Lean Six Sigma utilizes two primary methodologies—DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) for process improvement and DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) for designing new processes or products.
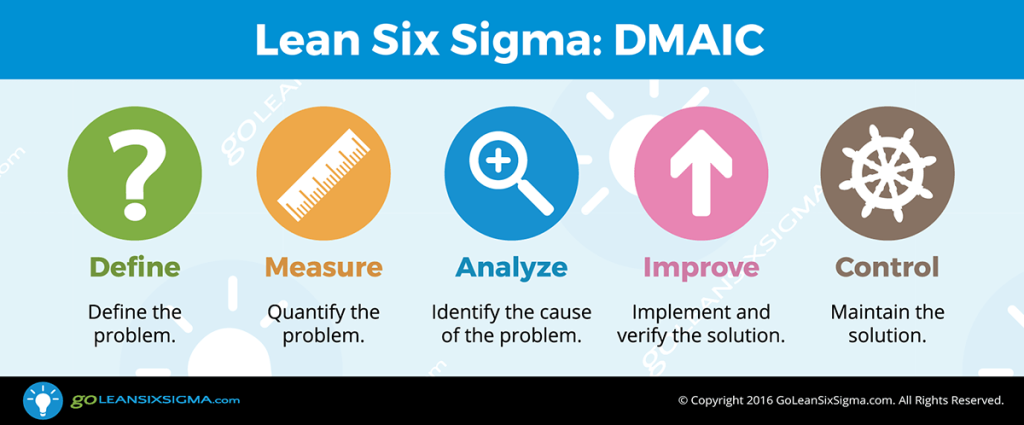
Phases of DMAIC
- Define: Clearly define the problem, project scope, and customer requirements.
- Measure: Collect data to quantify the current process performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Analyze: Analyze data to identify root causes of defects or waste.
- Improve: Develop and implement solutions to address identified issues and optimize the process.
- Control: Establish controls to maintain improved process performance over time.
Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
- Waste Reduction: Lean principles help eliminate waste, leading to cost savings and increased efficiency.
- Defect Reduction: Six Sigma principles reduce defects, improving product and service quality.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Meeting customer needs consistently leads to greater satisfaction and loyalty.
- Faster Processes: Streamlined processes lead to shorter cycle times and quicker deliveries.
- Increased Profitability: Reduced costs and improved quality contribute to higher profitability.
Challenges in Implementing Lean Six Sigma
Implementing Lean Six Sigma successfully may encounter challenges such as resistance to change, lack of data, and the need for extensive training. However, organizations that persevere often reap substantial rewards in terms of efficiency, cost savings, and customer satisfaction.